-Original content, please do not reprint.
What is a capacitor?
A capacitor is a fundamental linear electronic component with two electrical plates when there is a voltage difference between the two plates charge accumulation occurs.Capacitance is a physical quantity that expresses the ability of an electronic component (capacitor) to store charge and is also referred to as capacitance.Its unit is generally expressed in Farads (F) named after the British physicist Michael Faraday.
How capacitors work
• A capacitor acts like a storage tank that releases electricity to prevent power outages. Let's illustrate this with an actual circuit: if we rapidly switch on and off such a circuit without a capacitor, the light bulb will flicker. However, if we connect a capacitor to the circuit, even if we interrupt the circuit, the light bulb can still remain bright for a short period of time without continuously flickering, because the capacitance in the capacitor continues to release, supplying power to the circuit.
• Its main principle is due to two conductive plates made of metal in a capacitor.Their material is aluminum metal plates, and these metal plates are separated by insulating materials. The insulating materials are mainly used to control electrons, preventing them from flowing out of the capacitor at will. This allows our capacitor to connect with a battery, enabling electrons to be stored in the capacitor and then released when needed.
Capacitor parameters
The main parameters of the capacitor:
• First capacitance. indicates its ability to store charge. is usually expressed in Farads as F.
• Working voltage. The maximum voltage that can work is called the working voltage, which is represented by Ford V.
• Accuracy is also called tolerance. The difference between the actual capacity and the nominal capacity of a capacitor is called tolerance.
• Dielectric material. Capacitors, the two electrodes of a capacitor are usually filled with an insulating material called a dielectric or dielectric material. Different materials affect the performance of a capacitor.
• ESR Equivalent series resistance: Equivalent series resistance mainly refers to the impedance of AC signal, usually expressed in ohm.
• ESL Equivalent series inductance: It mainly refers to the inductive capacitance of high frequency signal, which is also expressed in ohm units.
Capacitor capacity conversion
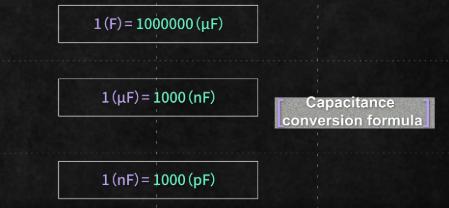
• Unit conversion of capacitance:1F=10^6uF=10^9nF=10^12pF?
• The basic unit of capacitance is farad (F):1F=10^3mF =10^6uF=10^12pF,1F=1000000μ
• Capacitor unit conversion:101=100pf,102=1000pf=1nf=0.001uf,103=10000pf=10nf=0.01uf,104=100000pf=100nf=0.1uf,105=100nf=1uf,106=10uf
• Inaccuracies:J=±5% K=±10% M=±20%,uF/ MFD nF pF/ MMFD,1uF / MFD 1000nF 1000000pF(MMFD),0.82uF / MFD 820nF 820000pF (MMFD),0.8uF / MFD 800nF 800000pF (MMFD),0.7uF / MFD 700nF 700000pF (MMFD),0.68uF / MFD 680nF 680000pF (MMFD),0.6uF / MFD 600nF 600000pF (MMFD),0.56uF / MFD 560nF 560000pF (MMFD),0.5uF / MFD 500nF 500000pF (MMFD),0.47uF / MFD 470nF 470000pF (MMFD)
Types of capacitors
Due to the different characteristics of capacitors made from various materials, a wide variety of capacitors have been developed.The differences among them lie in the variations in materials and performance parameters. Users need to select appropriate capacitors based on their specific products.Currently, the most widely used modern technologies are surface mount capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, and tantalum capacitors.
| Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor(MLCC) |  |
| Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitor |  |
| Aluminum electrolytic capacitor structure |  |
| CC |  |
| CL |  |
| CB |  |
| CBB |  |
| Monolithic ceramic capacitor(MLCC) |  |
| CY |  |
| CZ |  |
| CJ |  |
| CA |  |
Capacitor process
The manufacturing processes of capacitors made from different materials vary, and the most widely used and favored by mainstream technology are MLCC capacitors, which are also known as Multilayer Ceramic Capacitor. The terminal electrodes consist of a copper (Cu) substrate, a nickel (Ni) coating, and a tin (Sn) coating. Its structure is roughly as follows
Characteristics of capacitors
The capacitor has infinite resistance to DC current, meaning that the capacitor has the effect of isolating DC. The frequency of AC current can directly affect the resistance of the capacitor to AC current. Capacitors with the same capacity will exhibit different reactances to AC current at different frequencies. The formula for calculating reactance is as follows.
The application of capacitors
The application range of capacitors is very wide, most of the electronic devices we see have the presence of capacitors. Capacitors play a role in the field of electronics such as Wave filtering, Signal Filtering, bypassing, signal coupling, resonance, compensation, energy storage, DC isolation, etc., and it is one of the most important components in electricity.