-Original content, please do not reprint.
Microcontrollers are actually everywhere in our lives. They are found in almost every electronic device,including PCs, electronics, mobile phones, wearable devices, therapeutic equipment and even the aviation field. Every electronic device you can think of has their traces. It is an essential component for humans. So why is it so important? So what is a microcontroller?
Microcontroller definition
• A simple understanding of a microcontroller (MCU) is equivalent to a mini-computer. Unlike a computer, it does not require complex operating systems and hardware facilities. It features a random access memory (RAM) and electrical erasable programmable memory read-only memory (EEPROM). So what is the main structure of the microcontrollers?
Structure of microcontroller
There are three critical parts in the composition of a microcontroller.
• CPU:Here is its brain, which is responsible for controlling the key parts of the operating components.
• Memory:Microcontrollers have two types of memory: program memory and data memory. Program memory (also called flash memory) holds the code executed by the microcontroller. Data memory (also called RAM) holds the variables and data used by the microcontroller during operation.Commonly known as the "brain" of the computer,It is the core component responsible for executing command and control operations.
• RAM:A microcontroller contains volatile memory (RAM) (which, unlike program memory, stores temporary data that may be lost when the system loses power) and non-volatile flash memory (which stores the microcontroller's programming instruction set (firmware) .
• Peripheral:Microcontrollers may contain various auxiliary components such as input/output (I/O) interfaces (including timers, counters, analog-to-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog (DAC) signal converters (ADC)) and communication protocols (UART , SPI, I2C). Auxiliary devices may also include groups such as LCD screens, Ethernet connectivity ports, or interfaces to such modules.
• Video version: What is a microcontroller/what are its key components.
• Small size and low power consumption:As electronic devices become increasingly miniaturized, the volume requirements for original components are getting smaller and smaller, but the functional requirements are getting higher and higher. Microcontrollers are small in size, light in weight, and consume low power, so they are extremely efficient. This is why they are One of the reasons why it is used in wearables and devices that are primarily battery powered.
• low cost:In recent years, major microcontroller manufacturers have been lowering prices in order to seize the market, which has also led to microcontrollers becoming cheaper and cheaper, with higher performance ratios. Naturally, they are favored by consumer electronics, including industrial and The automotive field is also inseparable from microcontrollers.
• Flexibility and Programmability:Programmability also makes it easy for engineers to design products with various functions, which makes it very flexible and convenient.
• Integrated peripheral:Choosing a microcontroller can save the cost of many other peripheral devices. It often contains many internal and integrated ports, such as timers, ADCs, and communication ports, eliminating the need for additional ports.
• Time-honored operation:The fields of automation equipment and industrial control require products to respond and make decisions quickly in real time. Microcontrollers happen to meet this requirement. They can often process information simultaneously and immediately.Video version What is a microcontroller/Why should you choose a microcontroller?
History of the microcontrollers?
In 1971, the American Intel Corporation developed a microcontroller. It was a 4-bit microcontroller, called the i4004, that was successful, and at the same time Texas Instruments was not far behind, an engineer named Gary Boone was also working on this, and he designed an integrated circuit chip that It contains almost all the circuits needed to make a calculator (except the keyboard and display). The model number of this product is TMS1802NC, which can be programmed to perform different functions. But in fact, the first 8-bit microprocessor that the industry calls the first commercial use is Intel's 8008.
Evolutionary history of the microcontrollers
• The first microcontroller patent was issued in the Soviet Union in 1971 to M Kochren and G. Boone.
• The patent comes from Texas Instruments in 1971.Intel releases i8048 microprocessor in 1976.
• Motorola releases the mc6801 in 1978.Intel released the MK 18051, which is still popular today in 1980.MK 18051, still very popular today.
• This microprocessor has undergone some tweaks and modifications. At launch, it had a whopping 128,000 transistors. This is four times that of the previous version.
Types of microcontrollers
• 8-bit microcontroller:This is the most basic type of microcontroller and is currently the most widely used type of microcontroller. It is usually used in consumer products such as toys, small appliances and simple applications such as remote controls. They have limited processing power and memory capacity, but are easier to use and cheaper.
• 16-bit microcontroller:32-bit microcontrollers are the most powerful and feature-rich microcontrollers capable of handling large amounts of data and performing high-speed processing. They are used in applications such as gaming systems, multimedia equipment and high-end industrial automation.
• ARM microcontrollers:ARM microcontrollers are based on the ARM architecture and are used in a wide range of applications, including mobile devices, automotive systems, and industrial control systems.
• PIC microcontrollers:The PIC microcontroller is a product of Microchip. It is also a reduced-instruction microcontroller with a relatively small number of instructions. The mid-range PIC series only has 35 instructions, and the low-end one only has 33 instructions.
• AVR microcontrollers:AVR microcontroller is also a product of Atmel. The earliest one is AT90 series microcontroller.
• FPGA-based microcontrollers:These microcontrollers use field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) to provide highly customizable and flexible processing capabilities. They are commonly used in applications such as digital signal processing, video processing, and high-speed networking. For many microcontroller applications, FPGA is an ideal device because it is relatively low-cost, contains a large amount of embedded memory blocks, has enough I/O to handle almost all controller functions, and has rich registers.
what is Difference between microcontrollers and microprocessors
Differences in operating speed
• Microprocessor:Provide high speed and powerful computing capabilities for different applications. Modern computer processors operate in the gigahertz (GHz) range. This enables computer systems to perform complex mathematical calculations and return results quickly.
• Microcontroller:The speed of a microcontroller is much lower than the processing speed of a microprocessor. Microcontrollers have clock speeds ranging from kilohertz (kHz) to hundreds of megahertz (MHz).
There are many power consumption differences
• Microprocessor:Microprocessors usually run at a higher speed than microcontrollers, with the consequent disadvantage of higher power consumption and the need for the assistance of an external power supply. Due to the large number of additional components, the total power consumption of the computing system of the microprocessor unit will also be higher.
• Microcontroller:The characteristic of microcontrollers is to operate efficiently at the lowest power. Therefore, most microcontrollers have power saving functions, and microprocessors are relatively weak in this regard.
The operating system is different
• Microprocessor:Microprocessors require a specific operating system to function, or instructions must be issued to the microprocessor in assembly or binary language.
• Microcontroller:Microcontrollers have an advantage at this point, as they do not require an operating system to run. It is not ruled out that some other operating systems will be used to help make the microcontroller run more efficiently. In this regard, its flexibility is even higher.
Different costs
• Microprocessor:Microprocessors are cheaper because they only consist of a CPU, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and registers, which are relatively low cost.
• Microcontroller:Microcontrollers are generally more expensive because their internal architecture is more complex, making them more expensive to make.
Differences in connectivity
• Microprocessor:The microprocessor can handle high-speed USB 3.0 or Gigabit Ethernet data without the need for a secondary processor.
• Microcontroller:Microcontrollers require special processors to enable high-speed data connections.
They have different advantages and disadvantages and different uses. The main thing is that users need to choose the appropriate product according to their own needs. The application scenarios also determine the direction of the product, so it essentially comes from the differences in application scenarios.
Microcontroller working principle/function of microcontroller
In the whole working process of the microcontroller, CUP is its core part, and almost all actions need to be completed under its coordination. After receiving the signal through the external device, the microcontroller will be processed according to the preset program logic, such as calculation, decision making, etc. The processing results are stored in the memory, and the next step will output the control signal. Control the operating status of the equipment.
What are the naming rules for microcontrollers?
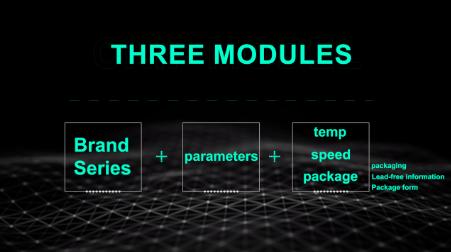
Part type, memory, core, device family, Memory size, origin, version, temperature, package and packaging form, let's apply it with the model number.
• THIS CHIP S9S12XS128J1MAA, S stands for automotive grade, 9 is the flash memory type, S12 is the core, XS is the device series, 128 is the flash memory size 128KB, J is the origin code, 1 is the version, M means the temperature range is minus 40℃-plus 125 ℃, AA represents package, indicating QFP80 package. Finally, there is an optional suffix. If the suffix contains R, it means tape and reel packaging, if not, it means pallet packaging.The one shown here is the new 16-bit microcontroller S12XS series, which is a compatible simplify version of the S12XE series.
![]() Q&A
Q&A
What is an example of microcontroller/components of microcontroller?
ST:ST microcontroller is currently the highest market share and the most widely used microcontroller brand, the main reason is that ST is low and high performance by the engineers to choose the love.
NXP:NXP acquired Freescale at the end of 2015. Since then, the two microcontroller products have become a brand. In recent years, NXP microcontrollers have performed very well on cars.
Renesas:In the first five years of the past decade, Renesas has been the largest supplier of MCU, mainly their microcontrollers have a wide range of applications, including the Internet of Things consumer electronics, industrial field.
Infineon:Infineon's widely known MCU is used in relatively high-end fields, such as factory automation, building automation, transportation and new energy vehicles.
What are the disadvantages of microcontrollers?
Its structure is relatively complex, and its application requires more skill.
While microcontrollers offer many link possibilities, they do have difficulty connecting with power devices.
The limited number of microcontroller execution is also one of its disadvantages.
The microcontroller can still be less powerful than the microprocessor or FPGA, despite its advantage in size.
The limited execution capacity is also due to its memory that is usually relatively limited.
Microcontrollers have few customized features, which show a disadvantage in the choice of unique products.
Not suitable for advanced signal processing (DSP): FPGA is more proficient in complex DSP tasks, although microcontrollers may not meet performance requirements.
Restricted I / O adaptation: Although microcontrollers have the underlying periphery, they may not provide similar levels of I / O adaptation to the FPGA, which is critical for a specific application.
What is a microcontroller used for?
Microcontroller after long-term development it can be used all over the fields, including consumer electronics, Internet of things, industrial automation equipment, new energy vehicles and so on, and microcontrollers are all kinds of various, selection needs to choose microcontroller according to the needs of each product.
What is the development trend of microcontrollers?
AI:Artificial intelligence is now used in a wider range of applications, has slowly become an inevitable trend of development, microcontroller also follow the strategy evolution, the edge of the artificial intelligence computing is the key to the technology, microcontroller with dedicated artificial intelligence hardware accelerator, such as neural processing unit (NPS) and tensor processing unit (TPS), perform complex ML algorithm, the minimum power consumption. This evolution opens up new areas for autonomous systems, smart sensors, and intelligent automation.
The future puts more emphasis on high connectivity:Under the requirement of the Internet of everything, microcontrollers must be highly connected, microcontrollers need to integrate more linked technologies, traditional wired interfaces such as Ethernet and CAN bus to advanced wireless technology, it is more and more important to integrate multiple communication protocols in microcontrollers.
Security threats will grow in the future:Sensitive data including personal information with the Internet to artificial intelligence, more exposed to ris