| What is a potentiometer |
| The function and application of potentiometer |
| Structure of potentiometer |
| Disadvantages of potentiometers |
- Original content, please do not reprint.
What is a potentiometer
A potentiometer (potentiometer) or voltage regulator, sometimes referred to as a pot or variable resistor, is a device that maintains its original characteristics even after prolonged use.
It consists of an adjustable sliding contact and a fixed resistor, and by moving the sliding contact to change the resistance value between the two terminals of the potentiometer,
the voltage or current in the circuit can be altered.
The function and application of potentiometer
1: Use RTD or TC sensors for linear and electronic temperature measurement;
2: It can convert the change of linear resistance to a standard analog current/voltage signal;
3: Power supply and signal isolation of secondary transmitter;
4: Use standard simulation output for process control;
5: Flow separation of analog signals and measurement of flow signals.
The application of potentiometers is very extensive playing a role in many fields. Potentiometers are widely used to monitor and control voltage and resistance in production processes.
They can monitor the voltage changes of equipment in real-time ensuring the normal operation of the equipment. Potentiometers can measure key parameters such as material resistivity
and battery voltage so they are often used in scientific research experiments. In addition to these two application fields potentiometers are also used in automotive electronics such as in
the engine control system of cars where they are used to monitor and regulate the voltage and current of the engine.
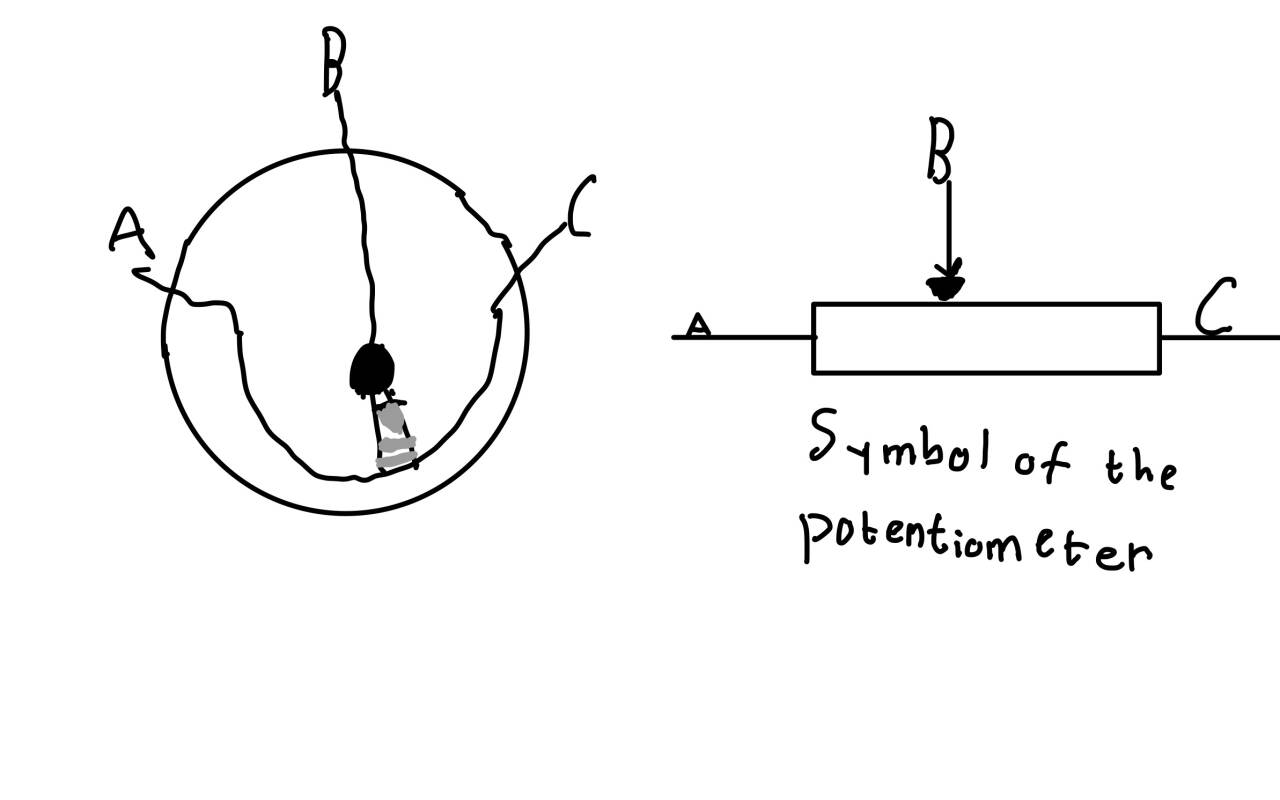
Structure of potentiometer
1 The core part of a resistor wire potentiometer is the resistor wire. The material is made of metal alloy, shaped linearly and wound in a spiral pattern, with the resistance distributed along
the wire. The two ends can be used to connect to the power supply, and changes in voltage will produce a potential difference across the resistor wire;
2. Sliding Contact: The sliding contact is a crucial part of a potentiometer used to measure voltage, typically consisting of a connecting wire and a contact point. The contact point can be a
small metal ball or a metal brush that slides over a resistor wire to change the position for voltage measurement;
3. Connection wire: The connection wire is used to connect the resistance wire and the circuit, and transfer the voltage to the sliding contact. The conductive performance of the connection
wire should be good to ensure the quality of signal transmission.
Disadvantages of potentiometers
The accuracy of potentiometers can be affected by temperature changes, not only that, wear and slippage as well as dirt can also cause instability and changes in this resistor. The good news is
that with the advancement of technology and materials, potentiometers can maintain their original characteristics for a long time after application. Although potentiometers have a high cost-performance
ratio, their disadvantage remains poor accuracy, making them unsuitable for precision control devices. Moreover, they come into contact with the operating hardware equipment, leading to unnecessary
wear and reducing their lifespan. Additionally, for a positioner to output digital signals to a controller, it needs to convert analog signals into digital signals before outputting, which is another disadvantage.