- Original content, please do not reprint.
What is the difference between TTL level and CMOS level
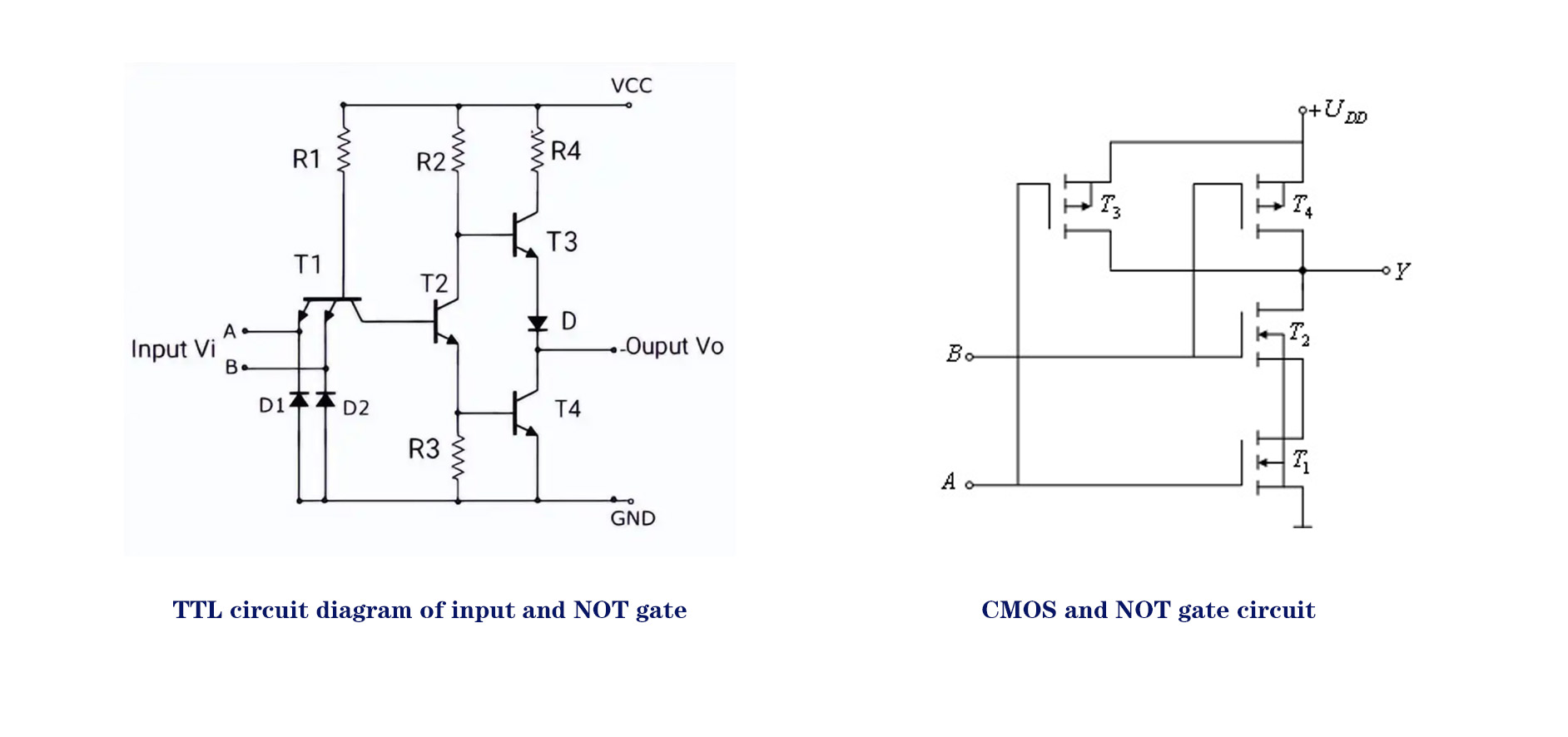
1. TTL Level High Level: 3.6V ~ 5V, indicating logic "1". Low Level: 0V ~ 2.4V, indicating logic "0". Unused Input: Can be left floating, default recognized as high level.
Power Requirements: Typically requires a stable 5V power supply, with high precision required for the power voltage.
2. CMOS Level High Level: Approximately 0.9 times the supply voltage (Vcc), indicating logic "1". Low Level: Approximately 0.1 times the supply voltage (Vcc), indicating
logic "0". Supply Voltage Range: Vcc can vary over a wide range (e.g., 3V to 12V), with relatively relaxed requirements for the power supply. Unused Input: Must not
be left floating; it must be fixed to a high or low level through pull-up or pull-down resistors, otherwise it may lead to logical confusion.
3. Main Differences Level Range: The high-level range of TTL levels is relatively narrow (3.6V to 5V), while the high level of CMOS levels depends on the supply voltage
and has a wider range. Power Adaptability: CMOS circuits have better power adaptability, capable of operating over a wide voltage range, whereas TTL circuits typically
require a stable 5V supply. Handling Unused Input Ports: Unused input ports in TTL circuits can be left floating, but unused input ports in CMOS circuits must be properly
handled and not left floating.
4. Compatibility The compatibility between TTL levels and CMOS levels can be achieved through appropriate level conversion circuits. For example, the high level of a TTL
output (3.6V to 5V) may not directly meet the high level requirement for CMOS inputs (0.9Vcc). In such cases, pull-up resistors or level converters can be used to resolve
this issue. From the above analysis, it is evident that there are significant differences between TTL and CMOS levels in terms of voltage range, power requirements, and
input/output characteristics. However, compatibility can be achieved through design in practical applications.
TTL level
The TTL level is usually based on the 5V power supply voltage, while the CMOS level is usually based on the 12V power supply voltage. Due to the different power supply
voltages of the two, direct connection will lead to the following problems:
1. The 5V TTL level cannot reliably trigger CMOS circuit:
The high level requirement of CMOS circuit is usually 0.9 times Vcc (that is, about 10.8V at 12V), while the high level output of TTL is only 3.6V ~ 5V, which cannot meet
the input requirements of CMOS.
This may cause CMOS circuit to fail to correctly identify the logic state, resulting in functional errors.
2, 12V CMOS level will damage TTL circuit:
The input voltage range of TTL circuit is limited, usually not more than 5V. If the 12V CMOS level is directly connected to the TTL circuit, it may damage the input end
of the TTL device.
3. Consequences of level mismatch:
Due to the large difference in voltage range between TTL and CMOS levels, direct connection will lead to incorrect signal transmission or even damage the device.
Therefore, TTL level and CMOS level cannot be directly compatible.
Solution: Level matching
In order to achieve the compatibility of TTL and CMOS circuits, the following methods can be adopted:
1. Level converter:
Use a dedicated level conversion chip (such as the 74HCT series) to convert TTL levels to CMOS levels, or vice versa.
2. Pull-up resistor:
Add a pull-up resistor to the TTL output to raise the high level to the voltage range required by the CMOS circuit.
3. Buffer or driver:
Use a buffer or driver chip to achieve level matching and signal isolation.
The above methods can effectively solve the problem of TTL and CMOS level mismatch, and ensure the correct transmission of signals and reliability of circuits.
TTL level standard
Level specification description
1. Output level
Low level (L): less than 0.8V, indicating logic "0".
High level (H): greater than 2.4V, indicating logic "1".
2. Input level
Low level (L): less than 1.2V, indicating logic "0".
High level (H): greater than 2.0V, indicating logic "1".
3. TTL device level characteristics
outlet end:
When the output is low, the voltage must be less than 0.8V.
When the output is high, the voltage must be greater than 2.4V.
input end:
When the input voltage is less than 1.2V, the TTL device recognizes it as logic "0".
When the input voltage is higher than 2.0V, the TTL device will recognize it as logic "1".
4. The meaning of the level range
Output level range: Ensure that the signal output by the TTL device can be correctly identified by other circuits.
Input level range: ensure that TTL devices can accurately judge the logic state of input signals and avoid logical errors caused by unclear levels.
Through the above specifications, TTL devices can work stably in digital circuits and achieve reliable signal transmission with other logic circuits.
CMOS level
output level:
Low level (L): less than 0.1 times the power supply voltage (Vcc);
High level (H): greater than 0.9 times the power supply voltage (Vcc).
incoming level:
Low level (L): less than 0.3 times the power supply voltage (Vcc);
High level (H): greater than 0.7 times the power supply voltage (Vcc).
This level specification is usually used to describe the input and output characteristics of CMOS circuits to ensure the correct identification and transmission
of logic states.
For instance
The 74LS series and 54 series belong to TTL circuits, while the 74HC series belongs to CMOS circuits. Although they have the same serial numbers and logical
functions, there are some differences in electrical performance and dynamic performance. For example:
1. Logical high level:
The logic high level of TTL circuit is usually **>2.7V**.
The logic high level of a CMOS circuit is usually **>3.6V**.
2. Level compatibility problem:
If the previous level of CMOS circuit is TTL circuit, because the high level output of TTL (>2.7V) may not be able to meet the high level requirement of CMOS
input (>3.6V), it may lead to unreliable logic state identification and hidden dangers.
Conversely, if the previous level of TTL circuit is CMOS circuit, because the high level output of CMOS (>3.6V) can meet the high level requirement of TTL input
(>2.7V), there will be no problem.
3. Performance differences:
Electrical performance: CMOS circuits consume less power, while TTL circuits have stronger driving power.
Dynamic performance: CMOS circuit has better anti-interference ability, while TTL circuit has faster switching speed.
Although the logical functions of 74LS, 54 series and 74HC series are the same, due to the differences in electrical performance and dynamic performance, special
attention should be paid to the level matching problem in practical applications to ensure the reliability and stability of the circuit.
Comparison of TTL and COMS circuits
1. Control mode
TTL circuit: is a current control device whose working principle depends on the drive of current.
CMOS circuit: it is a voltage controlled device, and its working principle depends on the change of voltage.
2. Speed and power consumption
TTL circuit:
Fast speed: short transmission delay time, usually 5~10ns.
High power consumption: due to high static and dynamic power consumption, it is suitable for scenarios with high speed requirements.
CMOS circuit:
Slow speed: The transmission delay time is longer, usually 25~50ns.
Low power consumption: the static power consumption is very low, suitable for low power consumption applications.
The relationship between power consumption and frequency: the power consumption of CMOS circuit is related to the pulse frequency of input signal. The higher
the frequency, the greater the power consumption, and the chip temperature will also rise, which is a normal phenomenon.
3. Locking effect of CMOS circuit
Lock-in effect (Latch-up):
When too much current is introduced into the input end of CMOS circuit, it may lead to a sharp increase in internal current and form a positive feedback loop.
Unless the power supply is cut off, the current will continue to increase. This phenomenon is called the locking effect.
When the locking effect occurs, the current inside the CMOS circuit may exceed 40mA, which is very easy to cause the chip burnout.
4. Summary
TTL circuit is suitable for high speed application, but the power consumption is higher; CMOS circuit is suitable for low power consumption application, but attention
should be paid to the locking effect and the influence of frequency on power consumption.
In the actual design, it is necessary to select the appropriate circuit type according to the specific requirements, and take corresponding protection measures (such as
current limiting, decoupling capacitors, etc.) to ensure the reliability and stability of the circuit.
Precautions for TTL circuit use
1. The impact of abnormal power supply voltage:
If the power supply voltage is too high or too low, the circuit may not work properly and even damage the device.
For example, too high a voltage may break down the semiconductor structure inside the device, while too low a voltage may prevent the circuit from reaching the
desired logic level.
2. Consequences of wrong power and ground connection:
If the positive and negative terminals of the power supply are reversed, it will lead to the wrong direction of current, which may cause excessive current and damage
the device.
Special precautions
1. Power supply voltage requirements for TTL circuit:
The TTL circuit usually uses **+5V power supply**, and the allowable voltage variation range is relatively narrow, generally 4.5V~5.5V.
Therefore, when using TTL circuit, it is necessary to ensure that the power supply voltage is stable and within this range to avoid abnormal operation of the circuit or
damage of the device.
2. Correctness of power connection:
When connecting the power supply, be sure to carefully check the positive and negative poles of the power supply, ensure that the positive pole of the power supply is
connected to the Vcc end of the circuit, and the negative pole of the power supply is connected to the ground (GND) end of the circuit.
Avoid excessive current and damage to devices due to incorrect power polarity.
The above precautions can effectively avoid circuit faults or device damage caused by power supply problems, and ensure the stability and reliability of the circuit.
Precautions for CMOS circuit use
The input of CMOS circuit is not allowed to be suspended, the main reasons are as follows:
1. Input potential is uncertain:
The unstable potential of the suspended input terminal may lead to the inability to determine the logical state of the circuit, thus destroying the normal logical relationship.
2. High input impedance is susceptible to interference:
When suspended, the impedance of the input end is very high, which is easy to be disturbed by external noise, resulting in circuit misoperation or logic error.
3. Static induction risk:
The suspended input end is easy to sense static charge, which may lead to gate breakdown and damage the device.
resolvent
In order to avoid the above problems, unused input terminals of CMOS circuits should be handled in the following ways:
1. Pull-up resistor: Connect the input terminal to the power supply (Vcc) through a resistor to make it fixed at high level.
2. Pull-down resistor: Connect the input terminal to ground (GND) through a resistor to fix it at a low level.
3. Direct connection: The unused input is directly connected to a fixed high or low level.
Through the above measures, it can ensure that the input end of CMOS circuit is in a definite logic state, and avoid the logic confusion, noise interference or electrostatic
damage caused by suspension, so as to improve the reliability and stability of the circuit.