| What is a memory |
| The role of memory |
| Memory classification |
| Types of memory sticks |
| Main parameters of memory stick |
| Memory encapsulation |
| Memory interface method |
| Application scope of memory |
-Original content, please do not reprint.
What is a memory
•Memory is a core component used to store programs and various types of data information, mainly responsible for the storage and reading of data. According to its function and purpose, memory can be divided into two categories: one is main memory, usually referred to as main memory or memory, which is mainly used to temporarily store running programs and data; the other is auxiliary memory, often called auxiliary memory or external memory, which is used to store a large amount of program and data information for a long time.
The role of memory
•The internal memory of a computer refers to a semiconductor memory device used to store data and instructions. It mainly includes two types: read-only memory (ROM, Read Only Memory) and random access memory (RAM, Random Access Memory). Among them, RAM can be further subdivided into static random memory (SRAM, Static RAM) and dynamic random memory (DRAM, Dynamic RAM). SRAM is often used in cache due to its high-speed characteristics; DRAM is widely used to form a computer's memory stick. On the other hand, ROM is mainly used to store firmware, such as startup programs in BIOS chips.
Memory classification
•Read-only memory ROM : Read-only memory (ROM) is a storage medium that is solidified by computer manufacturers through specialized technology to chips. Its characteristic is that once written, data can only be read and cannot be modified at will. The ROM family includes many types, such as mask ROM, programmable ROM (PROM), erasable programmable ROM (EPROM), electrically erasable programmable ROM (EEPROM), and flash memory (FLASH). This type of memory is often used to store program code that does not require frequent changes, such as the Basic Input and Output System (BIOS). A significant advantage of ROM is that the information it stores is nonvolatile and the data can be permanently preserved even in the event of power outage.
•Random memory RAM : Random access memory (RAM) is a volatile storage device used to temporarily store programs and data. When the power is turned off or the power is powered off, the information stored inside disappears. According to the differences in its manufacturing technology, modern RAM is mainly constructed using metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) technology and can be divided into two categories: static random access memory (SRAM) and dynamic random access memory (DRAM).
Types of memory sticks
•FPM DRAM: Fast Page Mode Dynamic Memory.
•EDO DRAM: Extended Data Out Dynamic Memory
•SDRAM:Synchronous dynamic memory
•RDRAM: Rambus DRAM high frequency dynamic memory
•DDR SDRAM: Double-rate synchronous dynamic random memory
•DDR II: Memory technology has achieved a significant breakthrough in performance, with its operating frequency being four times higher than traditional SDRAM memory, and has achieved twice the performance improvement compared to the previous generation of DDR memory.
Main parameters of memory stick
•Memory capacity: refers to the total amount of binary data that a single memory stick can store, usually in megabytes (MB) as the unit of measurement.
•Operating frequency: The operating frequency of memory refers to the rate at which the memory module transmits data within a unit of time, usually in megahertz (MHz) as the unit of measurement.
•Data bandwidth: Data bandwidth represents the ability of memory modules to transmit data within a unit of time, and is specifically reflected in the amount of data that can be processed by a single memory operation. As a key indicator for evaluating memory performance, its values directly reflect the data throughput efficiency of memory.
•Parity is the earliest widely adopted memory soft error detection scheme, and data errors are identified through simple parity verification. ECC verification (Error Checking and Correcting) is a more advanced error handling technology, which not only detects data errors, but also has the ability to automatically correct single-bit errors.
•CAS Latency: refers to the time interval required by the memory module to respond to the column address gate signal, which is usually quantized by the CL (CAS Latency) value. This parameter specifically reflects the number of clock cycles between the memory controller sending a column address gate signal to the actual start of data transmission, and is one of the important timing parameters to measure the memory access speed.
•Operating voltage: It is a key electrical parameter to ensure stable memory operation. Memory products from different generations have specific voltage specification requirements. Specifically, the standard operating voltage of SDRAM is 3.3V, the operating voltage of DDR1 memory drops to 2.5V, and the DDR2 memory drops to 1.8V. These voltage values are strictly designed standard parameters and must be strictly followed when used. Any voltage beyond the specified range may cause permanent damage to the memory module.
•SPD (Serial Presence Detect, serial presence detection): is an 8-pin 256-byte EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) chip integrated on the memory module. The chip stores key technical parameters of the memory module, including but not limited to detailed information such as operating frequency, storage capacity, operating voltage, row and column address configuration, and bandwidth. These preset parameters provide the necessary data support for automatic memory configuration at system startup.
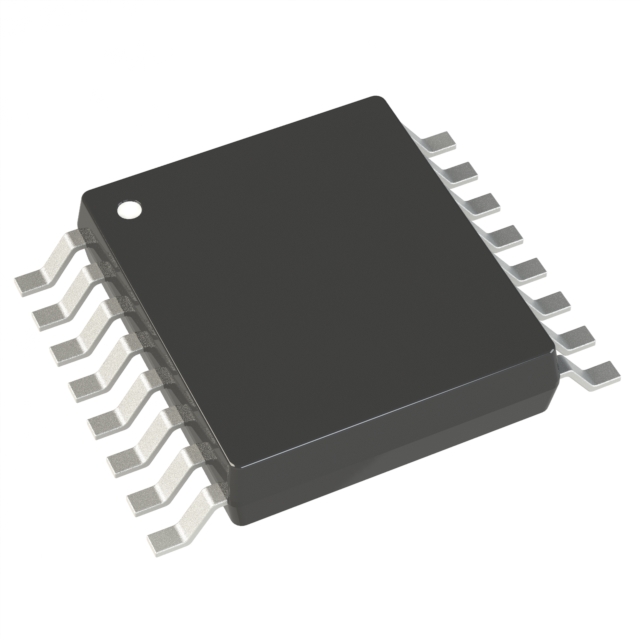
Memory encapsulation
•DIP
•SOP
•TSOP
•BGA
•Tiny-BGA
•mBGA
•CSP
Memory interface method
•SIMM 30 line
•SIMM 72 line
•SIMM 168line
•DIMM 184 line
•DIMM 240 line
•RIMM 184 line
Application scope of memory
•The application range of memory is extremely wide, and it penetrates almost all fields that require high-speed data processing and storage, such as automotive electronics, medical equipment, aerospace, etc. Almost all systems and equipment that rely on computer technology cannot do without the core component of memory.