| What is an attenuator? |
| The main purpose of attenuators? |
| Types of attenuators |
| Common attenuator parameters |
-Original content, please do not reprint.
What is an attenuator?
•An attenuator is an electronic component used to reduce signal strength. Its main function is to achieve signal attenuation by reducing the voltage, current or power of the signal. The device is usually composed of a resistor or a thermistor, which are capable of converting signal energy into thermal energy, thereby achieving an effective reduction in signal strength.

The main purpose of attenuators?
•Adjust the amplitude of the signal in the circuit
•In the measurement circuit using the comparative method, the device can directly read and display the signal attenuation degree of the measured network, thereby providing a convenient and accurate measurement method.
•To optimize impedance matching, when a particular circuit needs to maintain a relatively stable load impedance, an attenuator can be introduced between the circuit and its actual load impedance as a buffer for impedance variation. Generally, the attenuator is placed between the signal source and the load. It is a four-terminal network constructed from resistive elements. Its characteristic impedance and attenuation are both constant values independent of frequency and have a phase shift of zero.
•As the core component that realizes signal power regulation, impedance adaptation, precision testing and measurement, equipment protection, automatic gain adjustment, signal equalization, interference suppression and precise manipulation, the attenuator plays an indispensable role in many fields. Its application boundaries are broad, spanning multiple high-tech fields such as communication networks, testing equipment, radar systems, medical instruments, and aerospace technology.
Types of attenuators
•In the field of electronic engineering, fixed attenuators are known for their diverse structures, including several classic designs such as L-shaped, T-shaped, X-shaped and bridge T-shaped. L-type attenuators, due to their asymmetric characteristics, are often used to achieve accurate matching of impedances; while T-type, X-type and bridge T-type attenuators focus on signal attenuation function with their symmetrical structure. These attenuators can be divided into unbalanced attenuators and balanced attenuators according to their grounding method. One end of the unbalanced attenuator is connected to the ground, while neither end of the balanced attenuator is grounded. They each play a unique role in the circuit to ensure the accuracy and stability of signal processing.
Common attenuator parameters
•T-type attenuator

The resistance calculation formula of T-type attenuator is as follows:

•Pi attenuator

Calculation formula for resistor network:

•Bridged T-type attenuator
![]()
Resistance calculation formula:
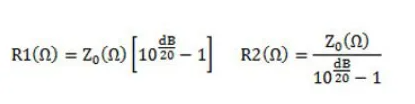
•Balanced attenuator

Resistance calculation formula:

•Reflective attenuator

![]()
The calculation formula is as follows: